Core Goal Progress
1. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
3% reduction in scope 1 & 2 emissions from 2018 to 2022
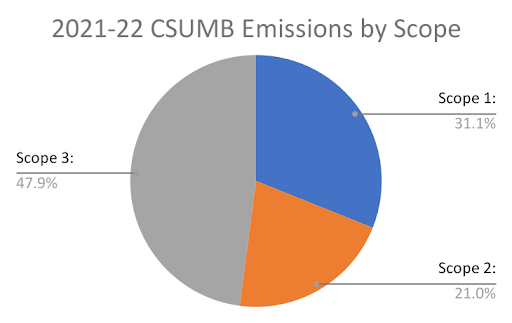
18% increase in scope 3 emissions (specifically waste related emissions and student commute - staff and faculty commute decreased
| All figures in MTCO2e | 2018-2019 | 2021-2022 |
|---|---|---|
| Scope 1: Natural Gas and Fleet Vehicles | 3,846.30 | 3,705.82 |
| Scope 2: Purchased Electricity | 2,599.26 | 2,566.35 |
| Scope 3: Commute, Waste, Misc. | 5,935.00 | 6,985.67 |
| Total | 12,380.56 | 13,247.84 |
2. Planting Trees
3. Diverting Waste
We have achieved 37% of the 90% goal for waste diversion by 2035
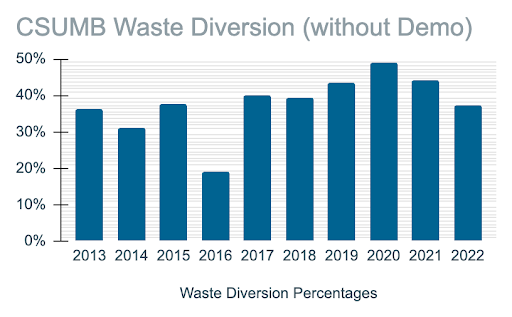
In 2021-2022
- 1,026 tons of material were landfilled
- 393 tons of material were recycled
- 192 tons of material were composted
Core Goals
In accordance with the first goal of the 2020 Inclusive Sustainability Plan, reducing the amount of Greenhouse Gas Emissions at our institution is of utmost importance to us, our students, and the Earth.
CSU Sustainability Policy Goals
- Promote the use of alternative transportation and/or alternative fuels.
- Reduce GHG emissions to 1990 levels by 2020.
- Reduce GHG emissions to 80% below 1990 levels by 2040.
- Increase on-site generation from 44MW to 80 MW by 2020.
- 33% Renewables by 2020.
Main Campus GHG Emissions from Energy
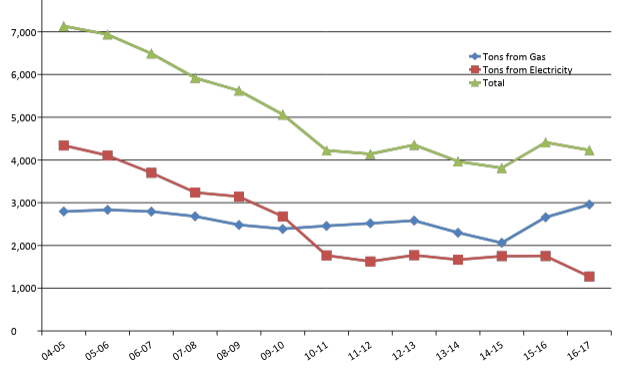
The chart on the left shows the greenhouse gas emissions from energy used on Main Campus. The Blue line represents tons from gas, the red line represents tons from electricity, and the green line represents the total of those two. The numbers on the bottom (x-axis) represent years, 2004-2005, 2005-2006, etc. The numbers on the left (y-axis) represent the tonnage in thousands, 1,000 tons, 2,000 tons, etc.
Energy STARS Report
The Sustainability Tracking, Assessment & Rating System™(STARS) is a transparent, self-reporting framework for colleges and universities to measure their sustainability performance.
Building Energy Consumption
Building Energy Consumption 2018 Score: 3.77/6.00 (about 63%)
MMBtu = One million British Thermal Units (BTU). A BTU is a measure of the energy content in fuel, and is is used in the power, steam generation, heating and air conditioning industries. One BTU is equivalent to 1.06 Joules.
2018 Performance Grid-purchased electricity 44,335 MMBtu Electricity from on-site renewables 5,486 MMBtu District steam/hot water (sourced from offsite) 0 MMBtu Energy from all other sources (excluding transportation fuels) 0 MMBtu Total 49,821 MMBtu Percentage reduction in total building energy consumption (source energy) per unit of floor area from 2009: 13.64%
Energy use standards and controls employed by CSUMB: No heat above 68F nor cool mechanically below 76F
Light Emitting Diode (LED) lighting and other energy-efficient lighting strategies employed by CSUMB: Conversion of streetlights to LED
Clean and Renewable Energy
Clean and Renewable Energy 2018 Score: 0.19/4.00 (about .05%)
Total energy consumption (all sources, excluding transportation fuels), 2018: 116,255 MMBtu
Total clean and renewable electricity generated on site in 2018 and for which CSUMB retains or has retired the associated environmental attributes: 5,486 MMBtu
Non-electric renewable energy generated at CSUMB, 2018: 0 MMBtu
Electricity use, by source:
Source Percentage of total electricity use Biomass 4% Coal 0% Geothermal 4% Hydro 8% Natural Gas 39% Nuclear 18% Solar photovoltaic 20% Wind 6% Action Across Campus
Solar panels
CSUMB increased our sustainability by installing a 6.4-acre solar panel lot consisting of 3,900 panels off Seventh Ave near Butler Street. This generates roughly 16 percent of the energy consumed on campus, although this amount can vary depending on how much sun peeks through the fog. This energy is used throughout campus and helps meet our electrical needs through clean, renewable sunlight
 Solar panels at CSUMB
Solar panels at CSUMB Natural lighting in Joel & Dena Gambord Business & Information Technology Building
Natural lighting in Joel & Dena Gambord Business & Information Technology BuildingLighting fixtures
Over 275 outdoor light fixtures have been retrofitted with new fluorescent bulbs, which reduced energy consumption of the fixtures by 78 percent. This also eliminated an extra 75 metric tons of carbon dioxide from being emitted into the atmosphere!
CSUMB was honored at the 2011 Higher Education Sustainability Conference and received an award in the best energy retrofit category. Once again, the school is making every effort to show sustainable practices and did so in the new Tanimura & Antle Library by decreasing the amount of time the air conditioners were on, which decreased the energy consumption by roughly 20 percent.
Energy Tips
- Instead of turning up the thermostat, try putting on a cozy sweater.
- Try not to use a space heater- They use too much energy. Use blankets instead!
- Unplug “vampire loads”- Many electronics use energy even when they’re off, or you’re not using them.
- Cell phone chargers. (Unplug from the wall when you take your phone off the charger).
- Television and media sets left on idle while you’re sleeping.
- Go through manual doors when feasible- they use less energy than automatic doors.
- Revolving doors are the most efficient at keeping temperature regulated air inside.
- Turn off any lights you don’t need, especially in the early evenings.
- Use the stairs- they're good for your health as well!
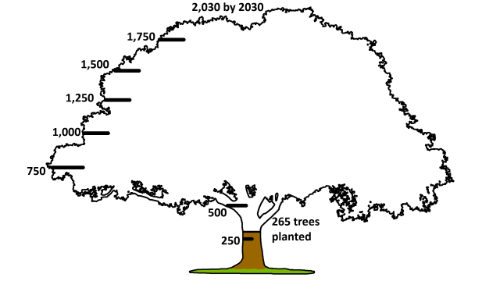
It is our goal to plant 2,030 trees by the year 2030, which requires active planning and action from various faculty, staff, and student groups on our campus.
Who is Involved?
- President's Sustainability Committee - Habitat Working Group: the habitat working group meets regularly and is responsible for planning, implementation, diligence, and analysis of the tree planting progress. For most of the 2020-21 AY, this group mapped out all potential tree planting areas on campus and started planting trees in the 2021-22 AY
- Return of the Natives (RON): RON supplies the trees used for planting at their on-campus nursery and has been an integral partner in organizing tree planting events
Where are Trees Planted?
The process of identifying "Where" we can plant trees took a lot of planning! After a year of meeting and mapping, the Habitat Working Group of the President's Sustainability Committee has located all potential sites for tree planting:
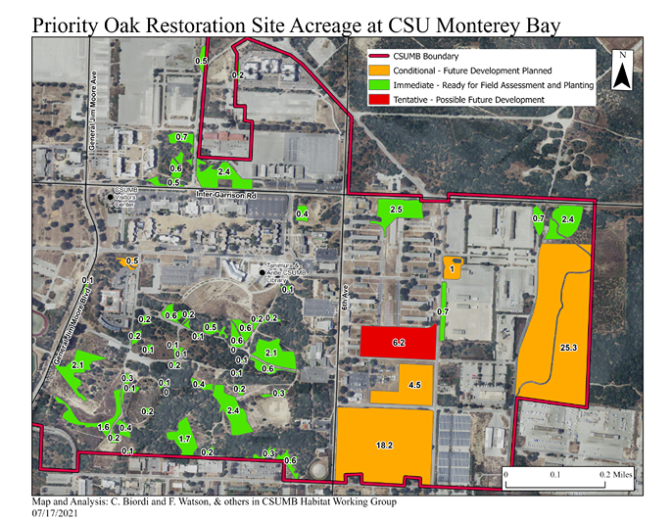
As of the 2021-22 Academic Year, tree planting has started at a few of the planting sites, as
seen in the next map:
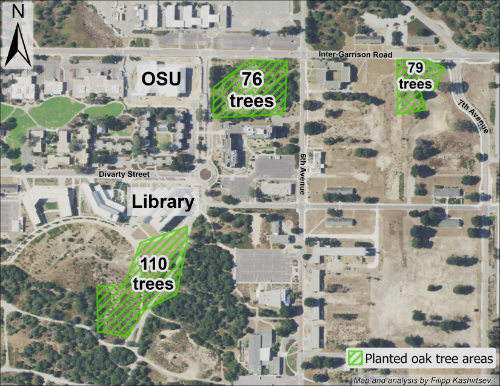
A map showing the locations and number of coast live oaks (Quercus agrifolia) planted on CSUMB campus since 2020.
Tree Planting Meter
Look at our current progress, as of July 2022, towards meeting our goal of planting 2,030 trees by 2030 goal:
The state of California has mandated to divert at least 75% of waste-related materials by 2020. Although the campus has historically met this requirement based on the high demolition and construction diversion, the daily practices of the campus community will need to improve to continue to meet these goals. Implementing programs that allow students to benefit from reuse initiatives enhances student success and helps the University meet its state mandate.
What Goes Where
The Monterey Regional Waste Management District is a one-stop shop to learn more about how to dispose of your waste in Monterey County properly and here at CSUMB. Visit the resources at the MRWMD webpage to learn more.
To learn "What Goes Where" for Monterey County, you can also download a smartphone application to help you properly divert your waste. Visit the What Goes Where webpage for more information.
STARS Report
The Sustainability Tracking, Assessment & Rating System™ (STARS) is a transparent, self-reporting framework for colleges and universities to measure their sustainability performance.
Planning Documents
Materials Management and Conservation Plan
This Climate Action (CAP) presents CSUMB’s strategy for reducing green house gas emissions associated with our operations and includes a baseline study which measures where we are in this effort, tracking our carbon footprint.
CSU Monterey Bay initiated a process to update its campus master plan in 2016 and drafted a version of it in 2017. The master plan envisions the future of our campus as it grows over the next 20 years. The Climate Action Plan Goals of 2020 demonstrate the current ways that CSU Monterey Bay hopes to enhance their sustainability efforts.
The American College & University Presidents' Climate Commitment (ACUPCC) is an effort to address global warming by creating a network of colleges and universities that have committed to neutralize their greenhouse gas emissions and accelerate the research and educational efforts of higher education to equip society to re-stabilize the earth’s climate.
The California State University (CSU) are major consumers of energy and natural resources. Therefore, CSU has the responsibility to be a wise steward of resources by reducing the use of non-renewable resources and increasing energy efficiency. CSU is also committed to promoting the continued economic and ecological viability of the State.
In order to strengthen and provide structure around certain aspects of sustainability, the campus is integrating the 7-petal Living Community Challenge into the Master Plan.